Sanctions Watch Vol 63
In the latest edition of our Sanctions Watch weekly digest, we present significant updates on sanction watchlists and regulatory developments.
UK Introduces Open General Licence for AUKUS Nations, Boosting Military Trade
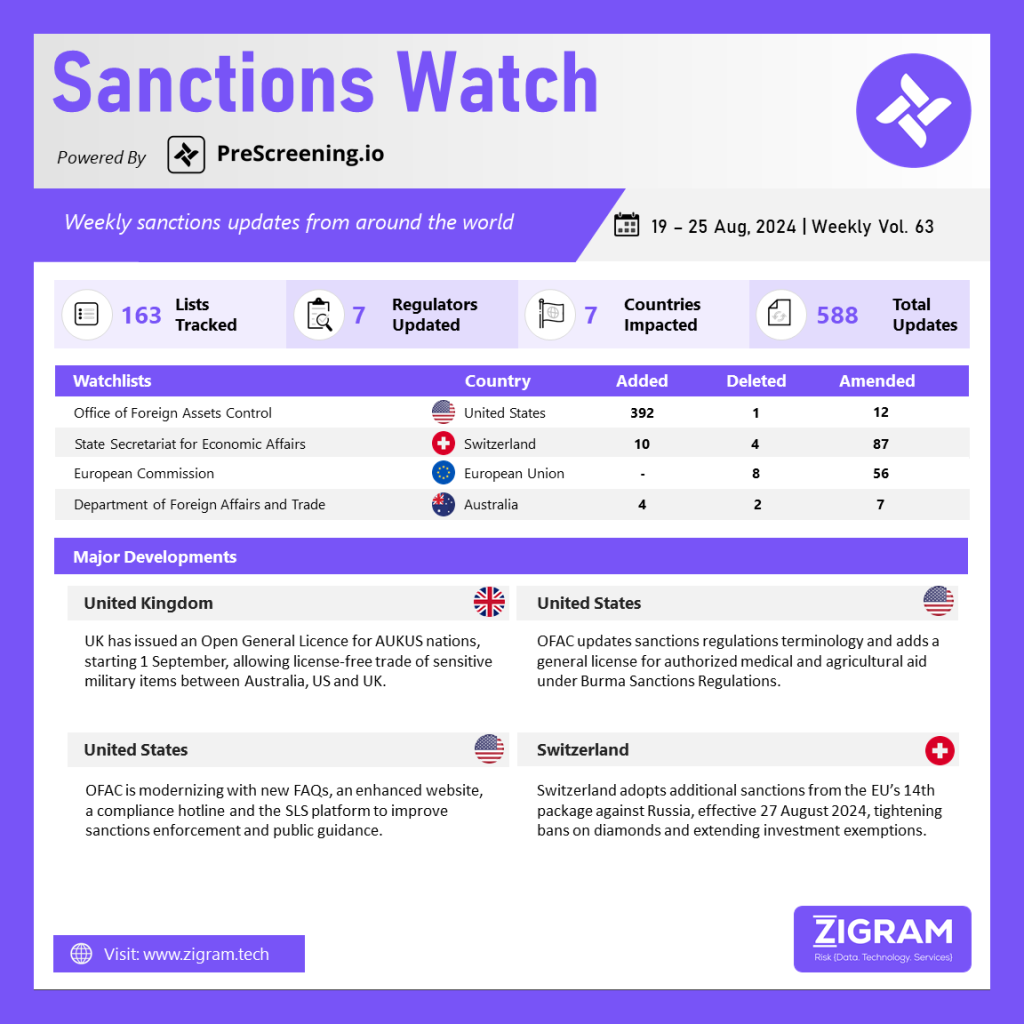
The United Kingdom has introduced an Open General Licence (OGEL) for AUKUS nations, effective September 1, enabling license-free trade of sensitive military items among Australia, the US, and the UK. Published on August 16, the OGEL facilitates the export of dual-use items, military goods, software, and technology, including re-exports to and from permitted destinations, even if incorporated into other products. This move follows the US Department of State’s recent notification to Congress about export controls for AUKUS partners, aligning Australia and the UK with US standards and allowing exemptions for top-secret nuclear technology.
The UK’s OGEL reciprocates this US exemption, covering similar goods and technology. UK exporters must be listed as Authorised Users by AUKUS nations, and controlled goods must be supplied to recipients on this list. The Export Control Joint Unit (ECJU) and the Department for Business and Trade (DBT) provided these details in their update.
OFAC Revises Burma Sanctions Regulations, Adds License for Medical and Agricultural Goods
The Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) is issuing a final rule to revise terminology and references in several sanctions programs’ regulations. This update includes adding a general license to the Burma Sanctions Regulations, providing agricultural commodities, medicine, medical devices, replacement parts and components for medical devices, or software updates for medical devices to individuals whose property and interests are blocked under the Burma Sanctions Regulations. These regulatory amendments are available for public review in the Federal Register and will become effective upon their publication on August 21, 2024.
OFAC Modernizes Infrastructure to Improve Sanctions Clarity and Compliance
The U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) is modernizing its infrastructure and stakeholder engagement strategies to enhance the clarity and enforceability of sanctions, as highlighted in Treasury’s 2021 Sanctions Review. By actively engaging with companies, organizations, and civil society groups, OFAC gathers valuable insights that inform new initiatives, such as updating frequently asked questions (FAQs), launching an improved website and search function, and enhancing public access to sanctions list data through the Sanctions List Service (SLS).
Additionally, OFAC has introduced the OFAC Reporting System (ORS) to streamline reporting processes and updated the Licensing Portal for better transparency. These efforts aim to improve the user experience, ensure compliance, and support OFAC’s mission of safeguarding U.S. national security through effective sanctions implementation.
Switzerland Implements New EU Sanctions Measures Against Russia Amid Ongoing Conflict
On 21 August 2024, the Swiss Federal Council decided to implement additional measures from the EU’s 14th sanctions package against Russia, effective 27 August. These actions respond to Russia’s continued military aggression and destabilizing activities in Ukraine, which threaten its sovereignty and security. Previously, on 9 July, Switzerland had added 69 individuals and 47 entities to its sanctions list. The new measures include clarifying international bans on Russian diamonds and extending deadlines for Swiss companies to withdraw from Russia legally. The Federal Council emphasizes the importance of effective sanctions enforcement and global coordination. Further measures from the EU’s 14th package, adopted on 24 June, are under detailed review and will be discussed by the Federal Council in due course.
Know more abou the product: PreScreening.io
Click here to book a free demo.
Sanctions Watch is a weekly recap of events and news related to sanctions around the world.
- #UnitedKingdom
- #GeneralLicence
- #MilitaryItems
- #DualUseGoods
- #NuclearTechnology
- #OFAC
- #SanctionsPrograms
- #Burma
- #SanctionsListService
- #NationalSecurity
- #SwissFederalCouncil
- #Russia
- #Ukraine
- #Switzerland
- #SanctionsWatch
- #InternationalSanctions
- #EconomicSanctions
- #RegulatoryCompliance
- #TradeCompliance
- #SanctionsEnforcement
- #SanctionsViolations
- #FinancialCrime
- #BansOnRussianDiamonds