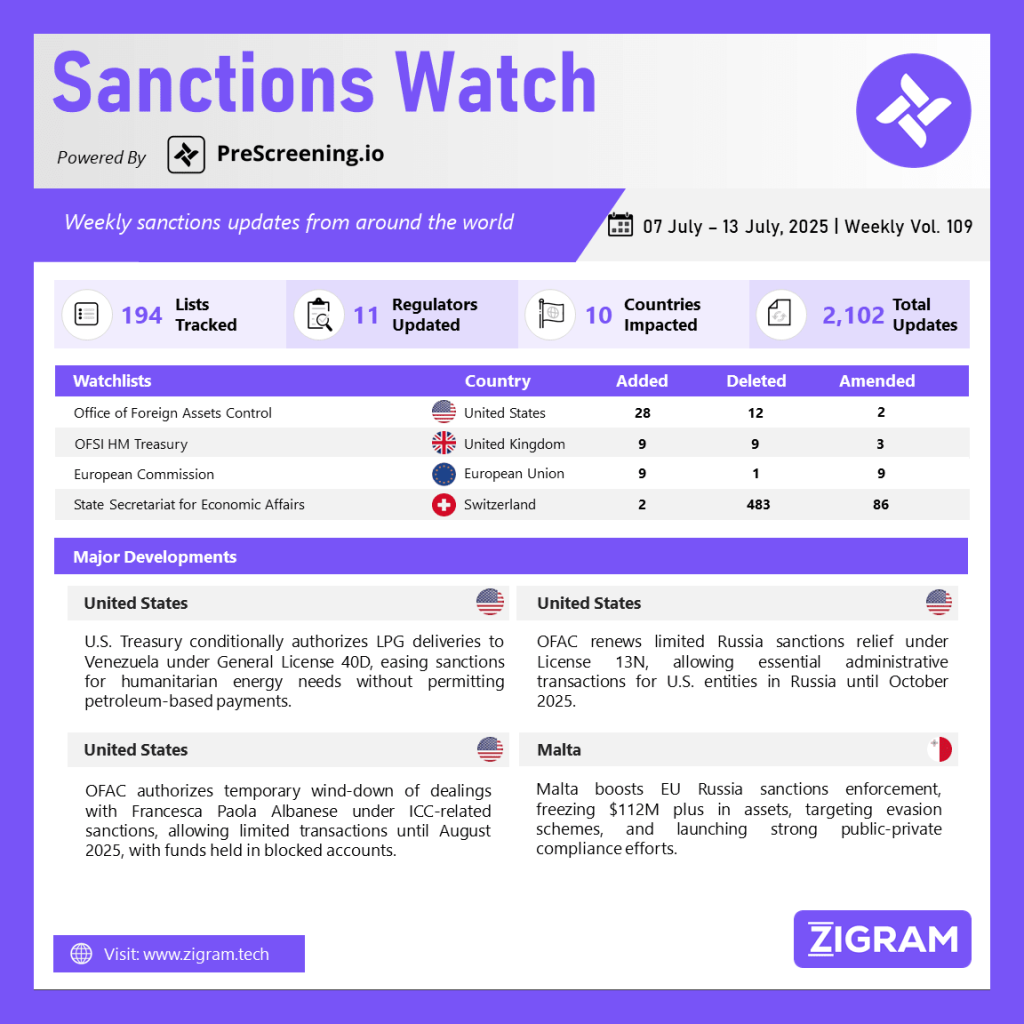
Sanctions Watch Vol 109
In the latest edition of our Sanctions Watch weekly digest, we present significant updates on sanction watchlists and regulatory developments.
1. U.S. Treasury Grants Conditional Authorization for LPG Deliveries to Venezuela Under General License No. 40D
The U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) issued General License No. 40D under the Venezuela Sanctions Regulations (31 CFR part 591). This license conditionally authorizes U.S. persons to engage in transactions ordinarily incident and necessary to the delivery and offloading of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) in Venezuela. Specifically, it permits transactions involving the Government of Venezuela, Petróleos de Venezuela, S.A., or entities in which PdVSA holds a 50% or greater ownership—activities typically prohibited under Executive Orders 13850, 13857, and 13884.
Importantly, the license does not permit payment-in-kind using petroleum or petroleum products, nor does it authorize transactions with other blocked persons under the Venezuela Sanctions Regulations—except those solely designated under E.O. 13884.
General License No. 40D replaces and supersedes the earlier General License No. 40C dated July 8, 2024. This measure reflects a nuanced shift in U.S. sanctions policy, likely aimed at addressing humanitarian or energy needs in Venezuela without fully relaxing broader economic restrictions.
Entities relying on this license must still comply with regulations from other federal agencies, including the Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security.
2. U.S. OFAC Renews Authorization for Limited Administrative Transactions in Russia Under General License No. 13N
The U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) issued General License No. 13N under the Russian Harmful Foreign Activities Sanctions Regulations (31 CFR part 587). This license authorizes U.S. persons and U.S.-controlled entities to carry out specific administrative transactions in the Russian Federation, which are otherwise prohibited under Directive 4 of Executive Order 14024.
The license permits the payment of taxes, fees, import duties, and the acquisition of permits, licenses, certifications, registrations, and tax refunds. These transactions are allowed only when they are deemed ordinarily incident and necessary to the routine operations of U.S. persons or entities in Russia. This authorization remains valid until 12:01 a.m. EDT on October 9, 2025.
However, the license explicitly prohibits any debits to accounts at U.S. financial institutions held by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, the National Wealth Fund, or the Russian Ministry of Finance. It also does not authorize any transactions involving persons or entities blocked under the Russian Harmful Foreign Activities Sanctions Regulations, unless specifically authorized.
General License No. 13N replaces and supersedes General License No. 13M dated April 7, 2025. The issuance of this license highlights OFAC’s ongoing efforts to balance sanctions enforcement with the need to allow essential administrative continuity for U.S. entities operating abroad, while maintaining restrictions on Russian state financial institutions amid ongoing geopolitical tensions.
3. OFAC Authorizes Temporary Wind-Down of Transactions Involving Francesca Paola Albanese Under ICC Sanctions General License No. 8
The U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) issued General License No. 8 under the International Criminal Court-Related Sanctions Regulations (31 CFR part 528). This license temporarily authorizes U.S. persons to engage in transactions that are ordinarily incident and necessary to the wind-down of any dealings involving Francesca Paola Albanese (Albanese) or any entity in which she holds a 50% or greater ownership interest.
Under this General License, transactions that would otherwise be prohibited under the ICC-related sanctions framework are permitted through 12:01 a.m. EDT on August 8, 2025. However, any payments made to Albanese or her associated entities must be deposited into a blocked account in accordance with OFAC’s standard procedures.
Importantly, this license does not authorize transactions involving any other persons or entities blocked under the ICC Sanctions Regulations unless separately approved by OFAC. It strictly limits permissible activity to wind-down efforts such as settling outstanding obligations or terminating contracts involving Albanese.
The issuance of this license demonstrates OFAC’s intention to provide an orderly process for disengaging from business or financial relationships with individuals subject to ICC-related sanctions, while maintaining the core integrity of the sanctions program. This move also underscores the Treasury’s nuanced approach in facilitating compliance transitions for U.S. persons and entities navigating complex international sanctions environments.
4. Malta Ramps Up EU Sanctions Enforcement with Asset Freezes and Crackdown on Evasion Schemes
Malta has significantly intensified its implementation of European Union sanctions targeting Russia in response to the ongoing war in Ukraine. These efforts align with the EU’s seventeen successive sanctions packages designed to restrict Russia’s war-financing capacity and hold enablers accountable.
Malta has adopted a multi-layered enforcement approach focused on identifying sanctioned individuals and entities, disrupting sanction evasion schemes, and delivering measurable outcomes. Notably, Malta has contributed to the freezing of over $112 million in offshore assets and taken decisive domestic actions, including freezing luxury yachts, two oil tankers, and shares of Malta-registered companies under Council Regulation (EU) No 269/2014.
In a high-profile case, Maltese authorities imposed a financial “firewall” on a sanctioned individual with ownership in a Malta-registered firm operating extensively across Europe. This control mechanism requires pre-approval for all transactions, ensuring that legitimate operations remain supervised and preventing the misuse of frozen funds.
Malta’s approach also emphasizes strong public-private collaboration through initiatives like the Joint Economic and Financial Sanctions Implementation Task Force and the Sanctions Compliance Forum. Monitoring is conducted in collaboration with the Financial Intelligence Analysis Unit, the Malta Financial Services Authority, and the Malta Gaming Authority, resulting in 211 compliance inspections.
Know more about the product: PreScreening.io
Click here to book a free demo.
Sanctions Watch is a weekly recap of events and news related to sanctions around the world.
- #SanctionsCompliance
- #GlobalSanctions
- #AdministrativeTransactions
- #AssetFreeze
- #BlockedAccount
- #EnergyPolicy
- #EUSanctions
- #ExecutiveOrder14024
- #Malta
- #OFAC
- #USForeignPolicy
- #USSanctions
- #USTreasury
- #VenezuelaSanctions
- #FinancialSanctions
- #FrancescaAlbanese
- #GeneralLicenses