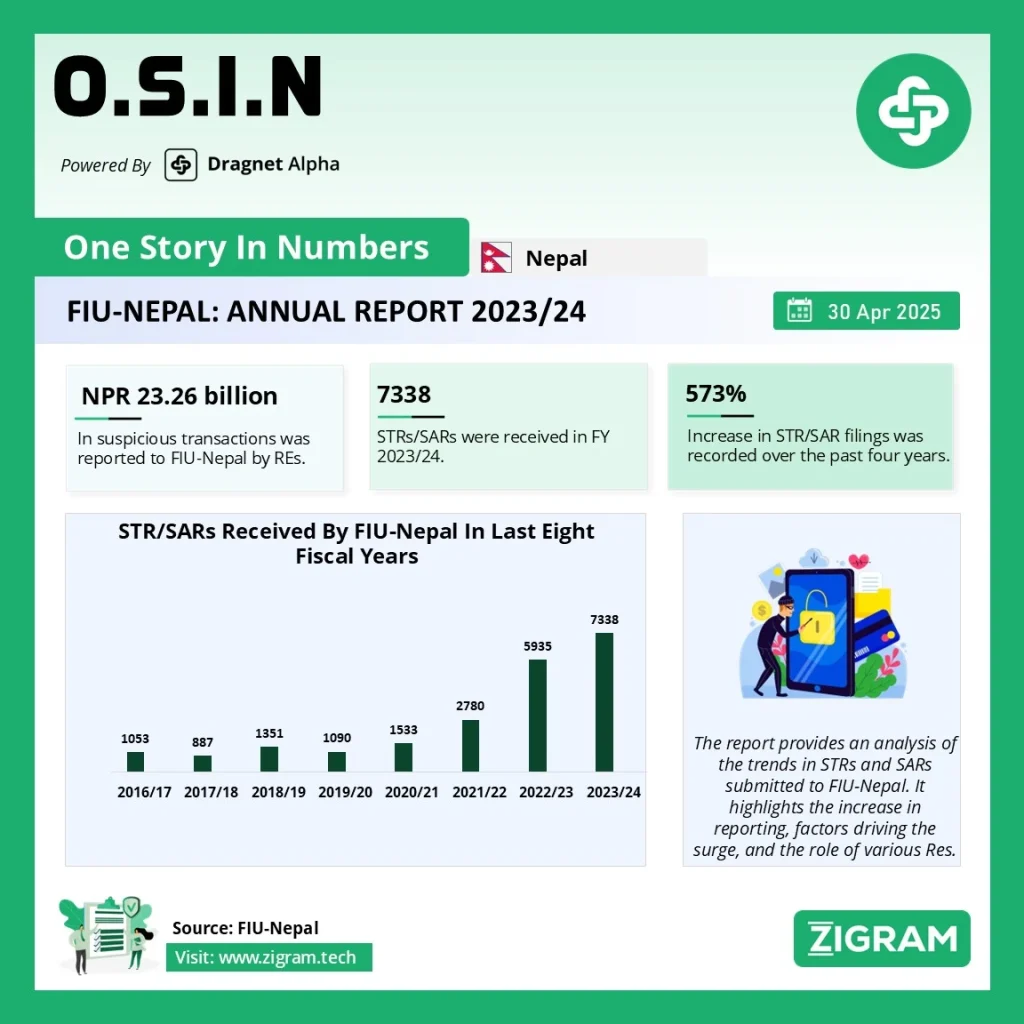
FIU-Nepal: A Significant Surge in STR/SAR Reporting and Analysis
In recent years, FIU-Nepal has experienced a remarkable increase in the number of Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs) and Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) received from Reporting Entities (REs). This surge is reflective of the country’s growing awareness and compliance with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Countering the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) regulations. The implementation of the goAML system, outreach programs, and the incorporation of more Reporting Entities (REs) have been key contributors to this upward trend.
The Rise in STR/SAR Reporting
FIU-Nepal has witnessed a substantial increase in the number of STRs/SARs in the past five years. In FY 2020/21, the total number of STRs/SARs received was 1,090, which escalated dramatically to 7,338 in FY 2023/24. The most significant rise occurred after the implementation of the goAML system in 2020/21. This system has made reporting more accessible and efficient, streamlining the process for REs and enhancing the overall AML/CFT efforts in Nepal.
The table below presents the total number of STRs/SARs received by FIU-Nepal over the last five years:
|
Reporting Institutions (REs) |
2019/20 |
2020/21 |
2021/22 |
2022/23 |
2023/24 |
|
Commercial Banks |
924 |
1,403 |
2,380 |
5,187 |
6,181 |
|
Development Banks |
93 |
64 |
119 |
257 |
491 |
|
Finance Companies |
1 |
12 |
19 |
44 |
217 |
|
Micro Finance Institutions |
0 |
3 |
44 |
28 |
12 |
|
Insurance Companies |
4 |
3 |
9 |
19 |
62 |
|
Remittance Companies |
52 |
29 |
187 |
146 |
126 |
|
Securities Companies |
14 |
18 |
8 |
46 |
52 |
|
Cooperative |
2 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
8 |
|
PSP/PSOs |
– |
– |
– |
202 |
181 |
|
Casino |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1 |
|
Government Agencies and Others |
0 |
1 |
11 |
5 |
7 |
|
Total |
1,090 |
1,533 |
2,780 |
5,935 |
7,338 |
Commercial banks have dominated the STR/SAR reporting in Nepal, accounting for 87.4% of the total reports in FY 2022/23 and 84.2% in FY 2023/24. The increased reporting from sectors like development banks, finance companies, and insurance companies reflects a broader commitment to AML/CFT compliance. Notably, reporting from Microfinance Institutions and Remittance Companies showed a decline in FY 2023/24, while the integration of Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs) in goAML is expected to bolster future reporting from these sectors.
The Role of FIU-Nepal’s Training and Outreach
A key factor behind the increasing number of STR/SAR submissions is the proactive role of FIU-Nepal in conducting outreach and training programs. These programs, often conducted in collaboration with regulatory bodies, stakeholders, and associations of REs, have raised awareness and enhanced understanding of the importance of timely and consistent reporting. Moreover, the launch of transaction monitoring systems by various REs to detect red flags and suspicious activity has significantly contributed to the surge in STR/SAR filings.
Monthly Reporting Trends
A closer look at the monthly receipt of STRs/SARs in FY 2023/24 reveals a trend aligned with the country’s economic activities. The lowest number of reports was recorded in Kartik (329), primarily due to festivals and reduced business operations, while Ashad saw the highest number at 1,136 reports. This fluctuation highlights the influence of seasonal factors and the fiscal year-end rush on the number of financial transactions and related suspicious activities.
Operational Analysis of STR/SARs
FIU-Nepal’s analysis of STRs/SARs plays a critical role in identifying potential money laundering and terrorist financing activities. In FY 2023/24, 7,338 STRs/SARs were received, with only 1,635 being analyzed due to resource constraints. Among the analyzed reports, 889 were disseminated to law enforcement agencies (LEAs), investigative agencies, and other relevant authorities. A total of 746 reports were postponed, primarily due to insufficient grounds for suspicion.
The growing number of reports poses a challenge for FIU-Nepal’s analytical capabilities, suggesting a need for improved processing systems. The integration of AI into goAML and enhanced analysis techniques could further strengthen FIU-Nepal’s efficiency in handling large volumes of STR/SARs.
Strategic Analysis: Unveiling New Trends
FIU-Nepal has also embarked on strategic analysis to uncover broader patterns and emerging risks in the financial sector. Recent reports, such as the analysis of suspicious tax evasion through personal bank accounts and cyber-enabled fraud (CEF), highlight new vulnerabilities in the financial system. The latter report provides valuable insights into the methods used in CEF, a growing concern due to its potential for large-scale financial crime enabled through digital platforms. By identifying key red flags and providing actionable recommendations, FIU-Nepal’s strategic reports contribute significantly to strengthening Nepal’s AML/CFT framework.
Conclusion
The surge in STR/SAR reporting in Nepal is a testament to the growing sophistication of the country’s financial institutions and their commitment to combating money laundering and terrorist financing. While the increased reporting is promising, the capacity of FIU-Nepal to analyze and disseminate intelligence must evolve in tandem to ensure that the rising number of reports translates into meaningful interventions. With the continued development of systems like goAML, improved training, and strategic analysis, Nepal is well-positioned to strengthen its AML/CFT efforts and protect its financial system from illicit activities.
By enhancing resources and incorporating advanced analytical techniques, FIU-Nepal can continue to lead in the fight against financial crime, ensuring that suspicious activities are identified and addressed promptly and effectively.
Read the full report here.
Please read about our product: Dragnet Alpha
Click here to book a free demo
- #FIUNepal
- #AML
- #CFT
- #AntiMoneyLaundering
- #FinancialCrime
- #GoAML
- #STR
- #SAR
- #SuspiciousTransactions
- #Compliance
- #NepalFinance
- #RegulatoryCompliance
- #FinancialMonitoring
- #MoneyLaunderingPrevention
- #AMLCompliance
- #SuspiciousActivity
- #FinancialSecurity
- #DigitalFraud