Anti Money Laundering News (09 Feb – 15 Feb 2026)
Welcome to this week’s edition of the Global AML News Weekly Digest. Here are the top stories making headlines around the world:
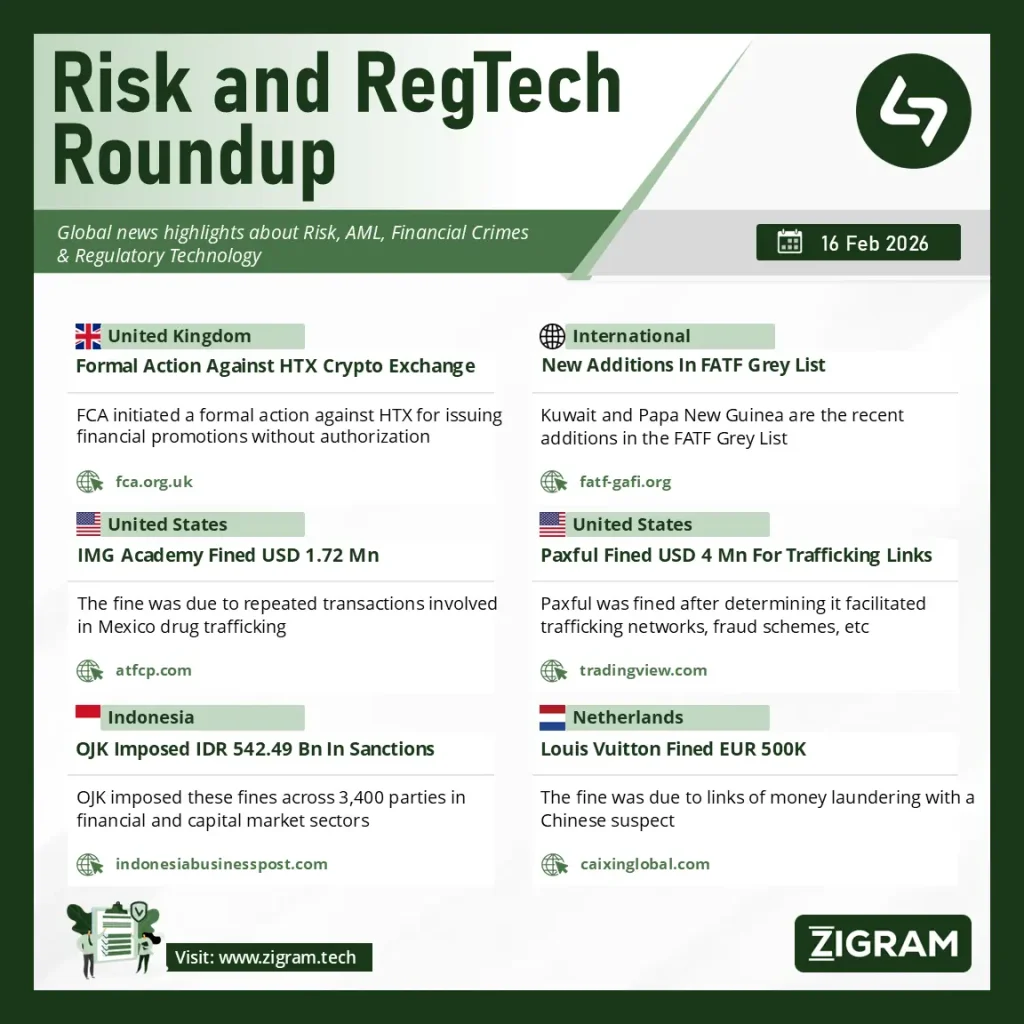
🇬🇧 FCA Moves Against HTX for Unlawful Financial Promotions in the UK
Financial Conduct Authority initiated formal action against crypto exchange HTX (formerly Huobi) for issuing financial promotions to UK consumers without proper authorization under Section 21 of the Financial Services and Markets Act (FSMA). The regulator found that HTX marketed cryptoasset services in the UK without approval from an FCA-authorized firm, violating the UK’s tightened crypto financial promotion regime introduced in 2023.
The FCA warned that the exchange’s communications failed to include mandatory risk disclosures and were not subject to compliance oversight. The action reinforces the regulator’s zero-tolerance stance toward offshore crypto platforms targeting UK retail investors.
This case signals enforcement escalation against unauthorized cross-border crypto marketing and underscores the requirement for firms to ensure local regulatory approvals before onboarding UK clients.
FATF February 2026 Plenary: Kuwait and Papua New Guinea Added to Grey List
Financial Action Task Force updated its list of Jurisdictions under Increased Monitoring (Grey List) following its 11–13 February 2026 Plenary.
New Grey List Additions (13 Feb 2026):
- Kuwait
- Papua New Guinea
Both jurisdictions were added due to strategic deficiencies in their AML/CFT regimes, including gaps in risk-based supervision, effectiveness of money laundering investigations, and implementation of preventive measures across financial and non-financial sectors.
Jurisdictions Remaining Under Increased Monitoring:
The Grey List continues to include countries such as Algeria, Angola, Bolivia, Bulgaria, Cameroon, Côte d’Ivoire, DRC, Haiti, Kenya, Lao PDR, Lebanon, Monaco, Namibia, Nepal, South Sudan, Syria, Venezuela, Vietnam, Virgin Islands (UK), and Yemen.
Removals:
No jurisdictions were removed from the Grey List during the February 2026 cycle.
High-Risk Jurisdictions (Call for Action – Black List):
- Iran
- Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK)
For financial institutions, the addition of Kuwait and Papua New Guinea triggers:
- Immediate country risk reassessment
- Enhanced due diligence requirements
- Review of correspondent banking exposure
- Transaction monitoring recalibration for affected corridors
FATF also reiterated supervisory focus on beneficial ownership transparency, proliferation financing controls, and virtual asset regulation.
🇺🇸 OFAC Fines IMG Academy $1.72M for Sanctions Violations Linked to Cartel-Connected SDNs
Office of Foreign Assets Control imposed a $1.72 million civil monetary penalty on IMG Academy for engaging in repeated transactions involving individuals designated as Specially Designated Nationals (SDNs) tied to Mexican drug trafficking organizations.
Between multiple instances, the institution processed payments and provided services benefiting blocked persons, violating U.S. sanctions regulations. OFAC determined the violations were non-egregious but highlighted deficiencies in sanctions screening, escalation procedures, and failure to detect red flags linked to high-risk individuals.
The enforcement action reinforces that non-financial entities must maintain robust sanctions compliance frameworks, including real-time SDN screening and enhanced due diligence for high-risk foreign counterparties.
The case underscores the convergence of AML and sanctions compliance obligations in cross-border transactions.
🇺🇸 U.S. Authorities Fine Paxful $4M Over Trafficking-Linked Crypto Transactions
U.S. authorities imposed a $4 million penalty on peer-to-peer crypto platform Paxful after determining it facilitated transactions tied to human trafficking networks, fraud schemes, and other illicit activities.
Investigators found that Paxful’s AML program lacked adequate transaction monitoring controls and failed to properly verify high-risk users operating across jurisdictions. The platform allegedly processed suspicious transactions without timely filing of required reports, allowing illicit actors to move funds through its ecosystem.
The enforcement highlights regulatory concern over P2P crypto marketplaces, which often operate with lighter compliance oversight than centralized exchanges. Authorities emphasized the need for stronger KYC enforcement, blockchain analytics integration, and suspicious activity reporting mechanisms.
The case signals intensified U.S. scrutiny of crypto platforms enabling anonymous or pseudonymous transfers.
🇮🇩 Indonesia’s OJK Imposes Rp542.49 Billion in Administrative Sanctions
Otoritas Jasa Keuangan announced it imposed Rp542.49 billion in administrative fines on 3,418 parties across Indonesia’s financial and capital markets sectors. The regulator also flagged 32 cases of suspected stock manipulation currently under investigation.
The sanctions relate to violations including reporting failures, disclosure breaches, market conduct irregularities, and non-compliance with supervisory requirements. OJK stated that enforcement efforts were intensified to protect market integrity and deter financial crime risks.
The scale of penalties reflects increased supervisory surveillance and cross-agency coordination in tackling market abuse and financial misconduct.
Financial institutions operating in Indonesia should expect tighter scrutiny of reporting frameworks, suspicious transaction monitoring, and governance oversight.
🇳🇱 Netherlands Fines Louis Vuitton Over Money Laundering Failures
Louis Vuitton was fined by Dutch authorities after prosecutors found failures in detecting suspicious cash transactions linked to a Chinese national involved in money laundering.
Authorities determined that the retailer did not adequately report unusual transactions involving high-value goods purchases, nor did it sufficiently scrutinize the source of funds in repeated luxury transactions. The deficiencies related to obligations under the Netherlands’ Anti-Money Laundering and Anti-Terrorist Financing Act (Wwft).
The case highlights regulatory expansion of AML enforcement beyond banks to designated non-financial businesses and professions (DNFBPs), particularly luxury retailers exposed to trade-based laundering risks.
Luxury goods sellers handling significant cash volumes must implement enhanced due diligence and mandatory suspicious transaction reporting protocols.
Stay informed with our weekly digest, bringing you the most impactful news from around the globe. Thank you for reading!
Subscribe to our weekly Newsletter – Click Here
Empower your organization with ZIGRAM’s integrated RegTech solutions – Book a Demo
- #AML
- #FinancialCrime
- #Sanctions
- #CryptoRegulation
- #FATF
- #OFAC
- #GlobalCompliance
- #RegTech
- #Enforcement
- #DNFBP